Materials & Metal Selection for Flashlight Parts

Choosing the right material for flashlight parts is very important. The material affects how strong and long-lasting the flashlight is. It also changes how heavy or easy to use it feels. For example, titanium is strong but light, so it’s durable and easy to carry. Stainless steel is super tough, great for hard jobs. Recycled plastics cost less and are good for the planet. They are also high quality and affordable. When picking materials for flashlight parts, think about what you need. Do you want it to be easy to carry or handle tough conditions? Choose what works best for you.
Key Takeaways
Picking the right material for flashlight parts is important. It impacts strength, weight, and how long it lasts. Think about your needs first.
Aluminum is a favorite for flashlight bodies. It is strong and light, great for daily use and outdoor fun.
Stainless steel is very tough and doesn’t rust. It works well for heavy-duty flashlights in rough conditions.
Polycarbonate lenses are light and don’t break easily. They are great for outdoor use. Glass lenses are clearer but heavier.
Recycled plastics are eco-friendly and used in flashlights now. They mix good performance with helping the environment.
Key Flashlight Parts and Their Material Needs

Housing and Body Materials
The flashlight's housing protects its inside parts. Picking the right material makes it strong, light, and weatherproof. Common materials are aluminum, stainless steel, titanium, and ABS plastic. Aluminum is light and strong, made from bauxite ore. But mining bauxite uses a lot of energy and harms nature. Stainless steel is very strong and rust-proof but heavier. Titanium is strong and light but hard to shape. ABS plastic is cheap and light but not as tough as metals.
Material | Strength | Durability | Corrosion Resistance | Machinability |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Stainless Steel | High | High | Excellent | Challenging |
Aluminum | Medium | High | Good | Easy |
Titanium | High | High | Excellent | Challenging |
Plastics (ABS) | Low | Medium | Good | Easy |
Lens Materials
The lens focuses and directs the flashlight's light. Lens materials need to be clear, strong, and long-lasting. Polycarbonate lenses are light and hard to break but scratch easily. Trivex lenses are also strong, clearer, and very light. High-index glass lenses are super clear but heavier and break easier.
Lens Material | Optical Properties | Durability Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
Polycarbonate | High impact resistance, low Abbe number | Easily scratched, requires scratch-resistant coating |
Trivex | High impact resistance, high Abbe number | Lightest material, requires scratch-resistant coating |
High-index Glass | Varies based on material, high refractive index | Heavy for glass, does not meet impact standards |
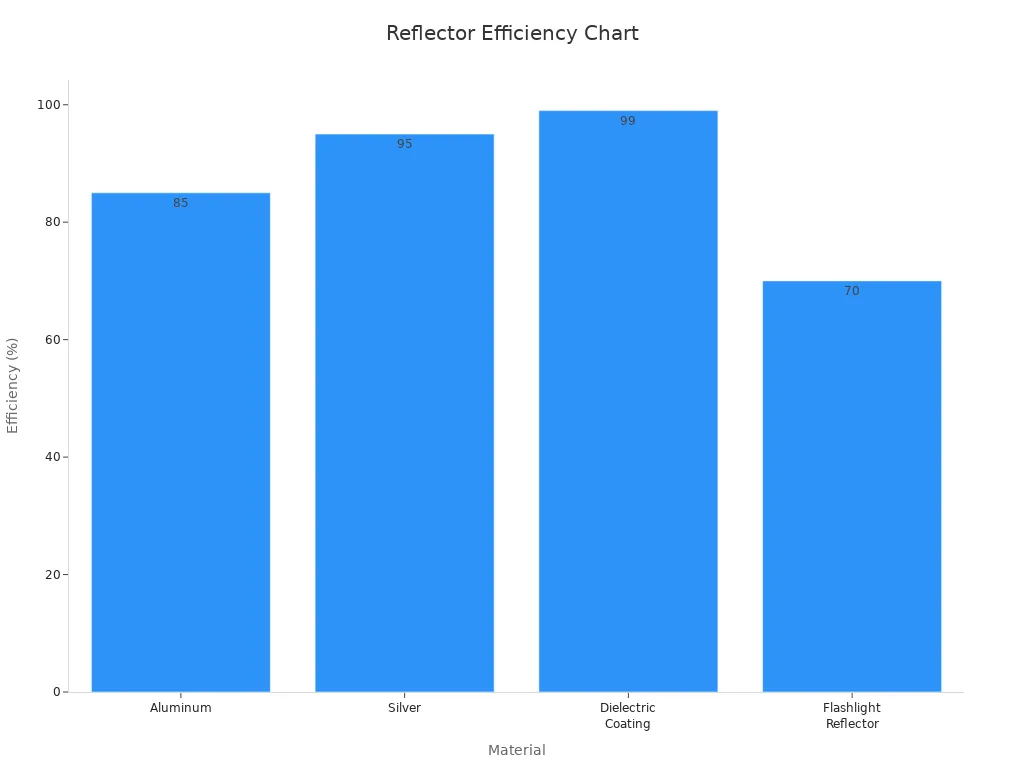
Reflector Materials
Reflectors help focus the flashlight's light beam. Aluminum reflectors work well, with 85% efficiency. Coated aluminum can reach 90%. Silver reflectors are better, up to 95%, but cost more. Dielectric coatings are the best, with 99% efficiency. Performance depends on how much light hits the reflector.
Circuit and Electronics Materials
The circuit is like the flashlight's brain. It controls the light and saves energy. Picking good materials makes it work well. Copper and gold are often used for connections. Copper is cheap and carries electricity well. Gold doesn’t rust, so it’s great for top flashlights.
Printed circuit boards (PCBs) are very important too. They are often made from strong, light fiberglass epoxy. This keeps the flashlight easy to carry and tough. LED flashlights need circuits that handle heat. Aluminum or copper layers in PCBs help cool them. This protects the LED and makes it last longer.
Wires and connectors are also key parts. Copper wires with covers are common. They carry electricity well and stop short circuits. Good electronics make sure your flashlight works when needed.
Power Source and Battery Compartment Materials
The power source is like the flashlight's heart. It gives energy to the light. Most flashlights use batteries, either reusable or throwaway. The battery compartment keeps batteries safe and easy to replace.
Plastic or metal is used for the compartment. ABS plastic is light, cheap, and strong. It protects batteries from damage. Aluminum is another choice. It’s tough and matches the flashlight’s body.
The compartment must stop leaks too. Rubber seals or gaskets are added for this. They block water and dirt, keeping the flashlight working in bad weather. A good power source and case make the flashlight reliable.
Common Materials for Flashlight Parts
Aluminum: Light and Strong
Aluminum is a common choice for flashlight bodies. It is light, making it easy to carry for daily use or outdoor trips. Even though it’s light, aluminum is strong and can handle drops or hits. This keeps the flashlight working in tough situations. Many makers use aluminum alloy to make it last longer and resist damage. Aluminum also cools down heat well, which is important for LED flashlights. This helps the flashlight work better and last longer.
Aluminum doesn’t rust, so it’s good for wet or rough places. It’s easy to shape, allowing designs like textured grips for better handling. These qualities make aluminum a flexible and affordable material for flashlight parts.
Stainless Steel: Tough and Rust-Free
Stainless steel is very strong and used for heavy-duty flashlights. It can handle rough use and harsh conditions without breaking. Unlike other metals, stainless steel doesn’t rust easily. Tests on types like AISI 316L and 304L show they resist rust even in tough environments. This makes stainless steel great for flashlights used near water or in wet areas.
New lightweight stainless steel alloys are strong and resist rust well. A special coating improves their ability to avoid rust spots, making them as good as older stainless steels. Stainless steel is heavier than aluminum, which might make it harder to carry. But its strength and long-lasting nature make it a good pick for tough flashlights.
Property | Lightweight Stainless Steels | Conventional Lightweight Steels | Commercial Stainless Steels |
|---|---|---|---|
Engineering Stress-Strain Curves | Data available in figures | Data available in figures | Data available in figures |
Elongation vs. Tensile Strength | Data available in figures | Data available in figures | Data available in figures |
Specific Strength vs. Pitting Potential | Data available in figures | Data available in figures | Data available in figures |
Titanium: Strong and Fancy
Titanium is a high-quality material that is both strong and light. It is stronger than aluminum but lighter than stainless steel. This makes it a great mix of toughness and easy carrying. Titanium doesn’t rust, even in salty water, so it’s perfect for outdoor or sea use.
Titanium is harder to shape than aluminum, but its special features make it worth the cost. Flashlights made from titanium are popular with people who like top-quality materials. Its shiny look also makes flashlights look stylish. If you need a strong material for tough jobs, titanium is a great choice.
ABS Plastic: Cheap and Easy to Carry
ABS plastic is often used for flashlight parts. It’s cheap and light, making it a good choice. Flashlight housings and battery compartments often use ABS plastic. It costs less than metals or fancy materials. This helps make flashlights affordable without losing quality.
ABS plastic is tough and handles drops or rough use well. It’s easy to shape into cool designs like grips or comfy shapes. Its light weight makes flashlights easier to carry for daily use or outdoor trips.
If you want a flashlight that’s cheap and easy to carry, ABS plastic is great. It’s strong and keeps the flashlight light for convenience.
Glass vs. Polycarbonate for Lenses
The lens focuses and directs the flashlight’s light. Picking the right lens material changes how clear and strong it is. Glass and polycarbonate are common choices for flashlight lenses.
Glass lenses are super clear and focus light really well. High-index glass lets light pass through easily but is heavier and breaks more easily. Glass lenses work best for careful tasks or safe places.
Polycarbonate lenses are light and hard to break. They’re great for outdoor use or rough conditions. But they scratch easily, so they need a special coating.
Think about how you’ll use your flashlight. Glass is clearer, while polycarbonate is tougher and lighter.
Pros and Cons of Material Choices for Flashlights
Weight vs. Durability
Picking flashlight materials means balancing weight and toughness. Light materials like aluminum and ABS plastic are easy to carry. They’re great for daily use or outdoor trips. But they might not survive hard hits as well as heavier ones. Stainless steel is super strong but adds weight to the flashlight. Titanium is both strong and light, making it perfect for high-quality flashlights. Think about how you’ll use your flashlight to decide what matters most.
Cost and Affordability
Material costs affect flashlight prices. ABS plastic is cheap and common in budget flashlights. Aluminum costs more but lasts longer and cools LEDs better. Stainless steel and titanium are pricier but very strong and rust-proof. For tough jobs, these materials save money by lasting longer. For casual use, ABS plastic or aluminum works fine and costs less.
Corrosion Resistance and Weatherproofing
Rust resistance is key for flashlights in wet places. Stainless steel and titanium don’t rust, even in salty air. Aluminum resists rust too but needs a special coating for extra protection. ABS plastic doesn’t rust but can weaken in sunlight or heat.
Tests prove how well these materials handle tough conditions. Simulated weather tests check durability. Rust tests like ASTM B117 show how materials handle moisture. Environmental chambers test long-term performance. These tests show why picking the right material keeps your flashlight working in any weather.
Heat Dissipation and Thermal Management
Managing heat is very important for flashlights, especially strong ones. LEDs make heat when they work, and controlling this heat helps the flashlight last longer. If heat isn’t managed well, the LED can wear out faster. The flashlight might also get too hot to use properly.
The materials in the flashlight body and heat sinks help control heat. Copper and aluminum are popular because they move heat well. Copper heat sinks cool LEDs quickly since they transfer heat fast. But copper holds heat longer, so it cools slowly after use. Aluminum heats up fast but cools down quickly, making it good for short uses.
Flashlight design also changes how heat is handled. For example, the Eagle Eye X6 flashlight has better heat control than the Ultrafire F13. The X6 has a thermal resistance of 0.31°C/W, while the F13 has 0.73°C/W. This means the X6 keeps the LED cooler, helping it work better and last longer. In tests, the X6 reached 93°C, and the F13 reached 102.3°C. Both stayed under the safe limit of 150°C.
Think about how you’ll use your flashlight when picking one. For long use, copper heat sinks are better. For short bursts, aluminum heat sinks work well. Choosing the right materials and design makes your flashlight reliable in different situations.
Emerging Trends in Flashlight Materials
Eco-Friendly and Sustainable Materials
Flashlight makers now use eco-friendly materials to help the planet. Recycled plastics and metals are common in new designs. Some flashlights even use solar power or water for energy. These ideas make flashlights useful for emergencies and outdoor fun while being green.
Supercapacitors are a new idea that avoids harmful waste. They are smaller, using less material, and are better for the environment.
LED technology has also made flashlights more energy-efficient. LEDs use less power and last longer, cutting down on battery waste. Rechargeable and solar-powered flashlights are becoming more popular as people want greener options.
Advanced Coatings for Durability
Special coatings make flashlight parts tougher for rough use. Epoxy coatings stick well and resist chemicals, great for work flashlights. Polyurethane coatings stop scratches, perfect for busy or rough places.
Coating Type | Key Benefits | Common Uses |
|---|---|---|
Epoxy Coatings | Sticks well, resists chemicals, great for tough jobs. | Factories, pipes, boats. |
Polyurethane Coatings | Stops scratches, resists chemicals, stays flexible. | Busy areas, factory floors. |
Ceramic Coatings | Handles heat, super hard. | Planes, cars, hot places. |
These coatings protect flashlights and make them last longer, even in tough spots.
Lightweight Alloys for Enhanced Portability
Lightweight flashlights are easier to carry and use. Aluminum alloys are popular because they are light but strong. Emergency workers like these flashlights for tough situations. Aluminum keeps flashlights light and durable for important tasks.
The YSMART MQ5 flashlight shows this trend. It uses Grade 5 titanium, which is strong, light, and stylish. This shows how people want flashlights that are easy to use but still high-quality.
Picking the Best Materials for Your LED Flashlight
Tactical Flashlights
Tactical flashlights are made for tough tasks. You might use them in emergencies, outdoor trips, or jobs like police work. These flashlights need strong and reliable materials. Aluminum is a favorite for the body. It’s light, strong, and doesn’t rust, making it great for rough conditions. Titanium is another good choice. It’s strong and light, perfect for extreme situations.
The lens is important too. Polycarbonate lenses are strong and resist breaking. They are lighter than glass and better for rough use. But they can scratch, so a special coating helps keep them clear.
Inside, copper or aluminum heat sinks are key. They control the heat from the LEDs. This helps the flashlight work well for a long time.
Everyday Carry (EDC) Flashlights
EDC flashlights are small and handy. You can carry them daily for simple tasks. These flashlights focus on being easy to use and portable. Aluminum is often used for the body. It keeps the flashlight light and strong. ABS plastic is another option. It’s cheap and can be shaped into comfy designs.
Most EDC flashlights have polycarbonate lenses. These lenses are light and tough, good for daily use. The battery compartment is usually made of ABS plastic. This keeps the flashlight light and affordable.
For EDC flashlights, pick materials that balance weight and strength. Aluminum alloys and good plastics are great choices. They make the flashlight easy to carry and still work well.
Heavy-Duty and Industrial Flashlights
Heavy-duty flashlights are made for hard jobs. You might use them in building work, factories, or inspections. These flashlights need materials that meet strict rules. Stainless steel is a top pick for the body. It’s super strong and doesn’t rust, even in tough places.
The lens must handle hits and scratches. Polycarbonate lenses with special coatings work best. They stay clear and last in rough conditions. Inside, copper heat sinks are very important. They move heat away from the LED, keeping it working well.
Some flashlights meet strict industrial rules. For example:
ASTM E3022-18 checks UV flashlights for brightness and beam quality.
ISO 3059 tests UV flashlights for inspections in special jobs.
Models like the TC1 UV-LED Flashlight Series follow these rules. This makes them reliable for tough work.
Picking the best materials for your flashlight helps it last. Strong materials like stainless steel or titanium are great for tough jobs. Lighter ones like aluminum or ABS plastic are easier to carry. Price matters too; expensive materials are good for hard tasks, while cheaper ones work for daily use.
Think about how you’ll use your flashlight. For outdoor trips, choose light and weatherproof materials. For work or factory use, pick strong and heat-resistant ones. Choosing the right materials makes your flashlight dependable and useful.
FAQ
What is the best material for a flashlight body?
The best material depends on how you’ll use it. Aluminum is light and strong, great for daily use. Stainless steel is very tough, perfect for hard jobs. Titanium is both strong and light, ideal for high-end flashlights. ABS plastic is cheap and light, good for simple tasks.
Why is heat dissipation important in flashlights?
Heat dissipation stops the LED and parts from overheating. Materials like aluminum and copper move heat away quickly. This helps the flashlight work well and last longer, even during long use.
Are polycarbonate lenses better than glass lenses?
Polycarbonate lenses are light and don’t break easily, great for outdoor use. Glass lenses are clearer and focus light better but are heavier and can break. Pick based on how you’ll use your flashlight.
How do coatings improve flashlight durability?
Coatings like epoxy or polyurethane protect against scratches and chemicals. They make flashlights tougher for rough conditions. Ceramic coatings handle heat well, great for powerful flashlights.
Can eco-friendly materials affect flashlight performance?
Eco-friendly materials like recycled plastics and metals work well and help the planet. Many flashlights use these without losing strength or quality. Sustainable materials are good for both users and the environment.
See Also
Utilizing CNC Machining for Tactical and Outdoor Flashlight Parts
Precision Manufacturing Techniques for OEM Handheld Flashlights
Understanding Various Stainless Steel Grades for Modeling Projects
The Anodizing Process for CNC Machined Aluminum Heat Sinks
CNC Machining Mastery: Tolerances, Prototyping, and Material Choices
About US
Follow Us
Your prototype holds unparalleled significance, and we deeply value its uniqueness. Collaborating with you during the preparation phase for running your prototype or parts is a commitment we gladly embrace. Whether it's a single part or a complex assembly, we are dedicated to selecting the optimal tools and pathways to bring your envisioned product to life.
At Precision Fab CNC Machining, we specialize in producing parts for prototypes, short runs, and high-volume production. Our prototyping machine capabilities extend across metal, plastic, and wood machining, with welding fabrication services available to complement and finalize your prototype if required.
Address
Address: Room320 10F, Building A,Nanshan international building, Dayawan District, Huizhou, Guangdong, 516001 China
Contacts
billy@timaycnc.com

